
Archaeologists, developed methods for the enrichment and analysis of nuclear DNA from sediments, and applied them to cave deposits in western Europe and southern Siberia dated to between approximately 200,000 and 50,000 years ago.
Isotopic and functional morphological analyses of early hominins are compatible with consumption of hard foods, such as mechanically-protected seeds, but dental microwear analyses are not. The protective shells surrounding seeds are thought to induce…

New discovery adds to the long list of important finds at Border Cave. The site has been repeatedly excavated since Raymond Dart first archaeologic worked there in 1934.
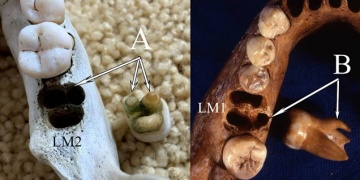
An article published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences with participation by the CENIEH refutes the similarities between the teeth of modern Asians and the Denisovans, an extinct human population that coexisted

"Fire was presumed to be the domain of Homo sapiens but now we know that other ancient humans like Neanderthals could create it," says Daniel Adler, associate professor in anthropology.
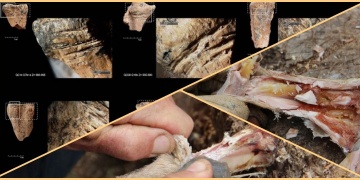
420,000 to 200,000 years ago, prehistoric humans at Qesem Cave were sophisticated enough, intelligent enough and talented enough to know that it was possible to preserve particular bones of animals under specific conditions, and, when necessary,…
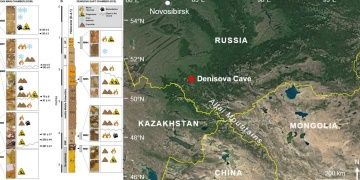
Micromorphology can help identify areas of sedimentary deposit that are most conducive to ancient DNA preservation and could be usefully integrated with DNA analyses of sediments at archaeological sites to illuminate features of their human and…

Genetic analysis has revealed that the ancestors of Homo Sapiens interbred with at least five different archaic human groups as they moved out of Africa and across Eurasia.

Neanderthals used resin 'glue' to craft their stone tools. Ethnographic evidence indicates that resin, which dries when exposed to air, is generally warmed by exposure to a small fire thus softened to be molded and pushed in position in the haft.
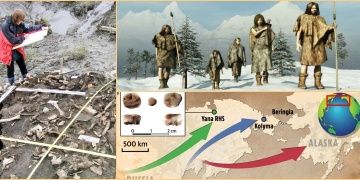
DNA from 31,000-year-old milk teeth leads to discovery of new group of ancient Siberians. Newly discovered ancient teeth dating back 31,000 years are evidence of a new ethnic group in human history and could change know about the first American…

Using computer simulations to discover where Neanderthals lived. Archaeologist Fulco Sherjon has used computer simulations to identify where and how Neanderthals lived in West Europe. What stood out was that they probably had lots of children and…

The jawbone, discovered high on the Tibetan Plateau and dated to more than 160,000 years ago, is also the first Denisovan specimen found outside the Siberian cave in which the hominin was uncovered a decade ago.






















 Milletvekili Aykut Kaya: Antalya Arkeoloji müzesi aynı yere yapılacaksa kamu israfı
Milletvekili Aykut Kaya: Antalya Arkeoloji müzesi aynı yere yapılacaksa kamu israfı  Ağrı Dağı'ndaki Nuh'un Gemisi oluşumu nasıl keşfedildi, dünyaya nasıl tanıtıldı?
Ağrı Dağı'ndaki Nuh'un Gemisi oluşumu nasıl keşfedildi, dünyaya nasıl tanıtıldı?  Bizanslı Kadınlarla Osmanlı Kadınları benzer kaderlere sahipmiş!
Bizanslı Kadınlarla Osmanlı Kadınları benzer kaderlere sahipmiş!  Zelve problemi: Önce turizm mi kayrılmalı yoksa kültürel ve doğal miras mı korunmalı?
Zelve problemi: Önce turizm mi kayrılmalı yoksa kültürel ve doğal miras mı korunmalı? 

