
Archaeologists, developed methods for the enrichment and analysis of nuclear DNA from sediments, and applied them to cave deposits in western Europe and southern Siberia dated to between approximately 200,000 and 50,000 years ago.
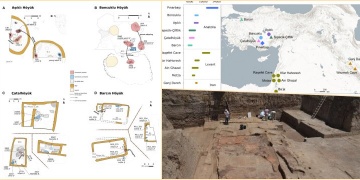
Neolithic Anatolian communities often buried their dead beneath domestic buildings,2 household composition and social structure can be studied through these human remains. Scientists, describe genetic relatedness among co-burials associated with…
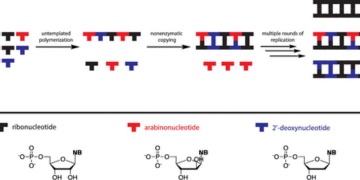
A Model for the Emergence of RNA from a Prebiotically Plausible Mixture of Ribonucleotides, Arabinonucleotides, and 2'-Deoxynucleotides
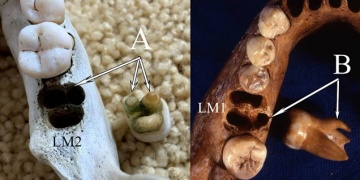
An article published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences with participation by the CENIEH refutes the similarities between the teeth of modern Asians and the Denisovans, an extinct human population that coexisted

120-year-old extinct Crimean lizard revealed by mitochondrial DNA: The western green lizard Lacerta bilineata was introduced to the Crimean Peninsula
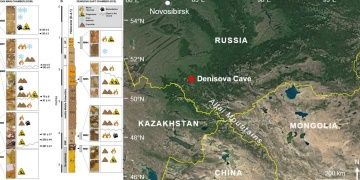
Micromorphology can help identify areas of sedimentary deposit that are most conducive to ancient DNA preservation and could be usefully integrated with DNA analyses of sediments at archaeological sites to illuminate features of their human and…

New analysis of ancient fish bones suggest aquaculture has deep historical roots in China.

Howard Hughes Medical Institute and Broad Institute researcher David Reich commented on the oldest ancient DNA Study made about the prehistory of South and Central Asia and arguesed: We can rule out a large-scale spread of farmers with Anatolian…

Genetic analysis has revealed that the ancestors of Homo Sapiens interbred with at least five different archaic human groups as they moved out of Africa and across Eurasia.

Ancient DNA has shed fresh light light on the origins of the legendary Biblical people who gave their name to mindless thuggery. It suggests they descended from migrants who crossed the Mediterranean and reached the shores of modern-day Israel,…
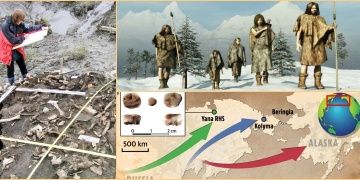
DNA from 31,000-year-old milk teeth leads to discovery of new group of ancient Siberians. Newly discovered ancient teeth dating back 31,000 years are evidence of a new ethnic group in human history and could change know about the first American…

The jawbone, discovered high on the Tibetan Plateau and dated to more than 160,000 years ago, is also the first Denisovan specimen found outside the Siberian cave in which the hominin was uncovered a decade ago.
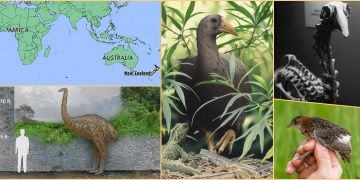
The ancestor of New Zealand’s most mysterious giant bird – the extinct adzebill – likely flew here from Madagascar, Africa, new research has revealed.

Milk proteins preserved in dental calculus indicate an early focus on Western domesticated ruminants rather than local species, but genetic ancestry analysis indicates minimal admixture with Western steppe herders, suggesting that dairy pastoralism…
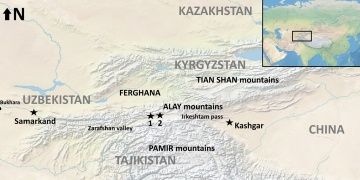
Recent archaeological survey reveals a millennia-long history of pastoral occupation of Alay from the early Bronze Age through the Medieval period, and a stratified Holocene sequence at the site of Chegirtke Cave.

Humans may have started growing cacao trees -- the source of chocolate -- about 3,600 years ago in Central America, a study has found. Cacao analysis dates the dawn of domesticated chocolate trees to 3,600 years ago
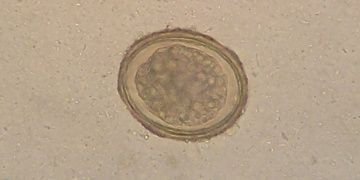
Molecular archaeoparasitology identifies cultural changes in the Medieval Hanseatic trading centre of Lübeck


























 Müzeler kültür yuvası olmaktan çıkıp birer "Fotoğraf Durağı"na mı dönüşüyor?
Müzeler kültür yuvası olmaktan çıkıp birer "Fotoğraf Durağı"na mı dönüşüyor?  Bitlis'teki Selçuklu Kalesi'nde Yapılan Kazılarda Sikke ve Seramikler Bulundu
Bitlis'teki Selçuklu Kalesi'nde Yapılan Kazılarda Sikke ve Seramikler Bulundu  Çaltılar Höyük'teki Arkeolojik Kazılar Devam Ediyor
Çaltılar Höyük'teki Arkeolojik Kazılar Devam Ediyor  Stratonikeia Antik Kenti'ndeki Roma Hamamında Restorasyon Tamamlandı
Stratonikeia Antik Kenti'ndeki Roma Hamamında Restorasyon Tamamlandı 

